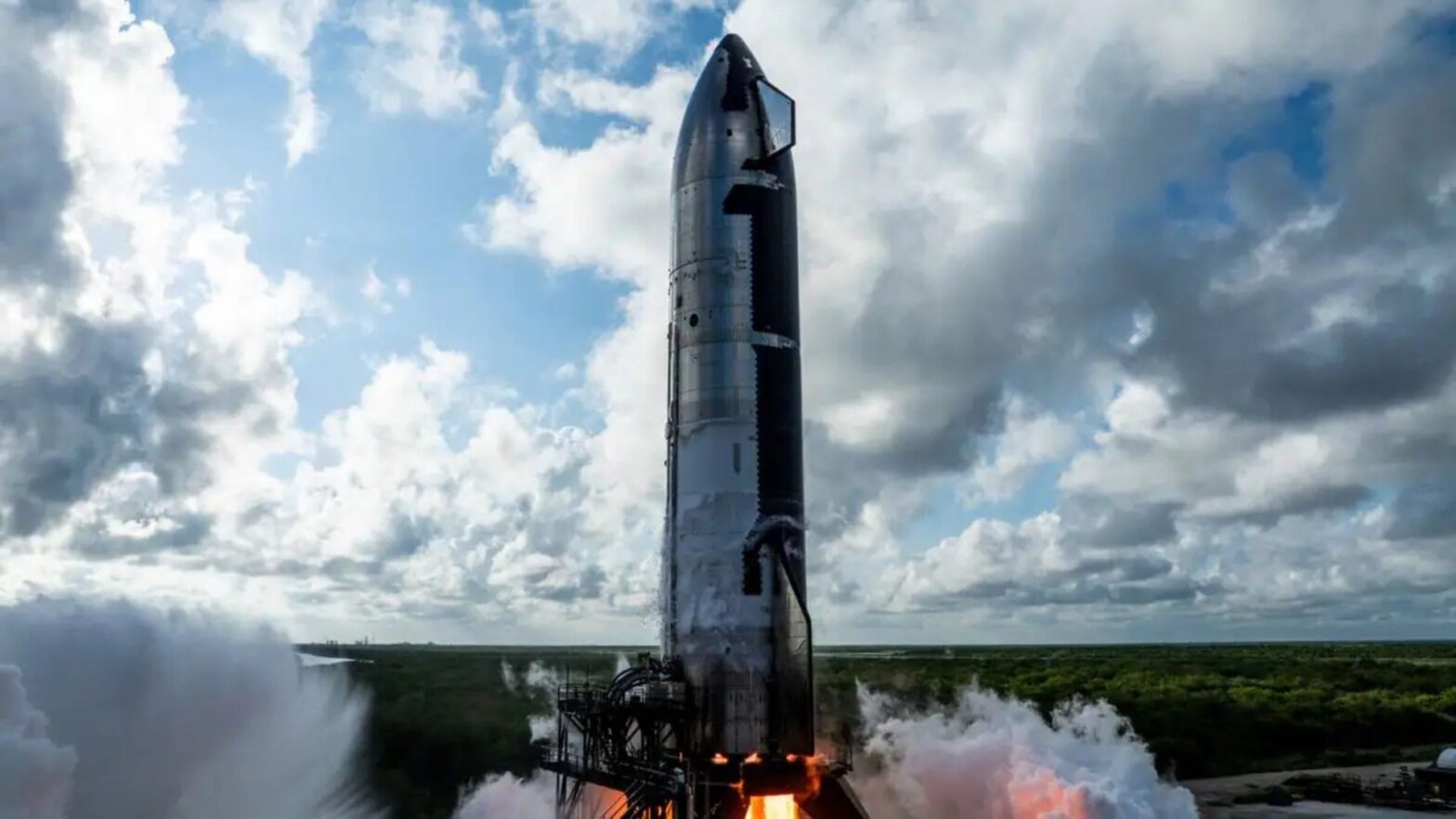
SpaceX is taking the next bold step in its ambitious Starship program with its upcoming sixth flight test, set for November 18, 2024. This marks a critical juncture for the company, as it continues refining the world’s most powerful rocket. With rapid testing cycles and groundbreaking milestones achieved in previous flights, this new launch represents more than just a routine check. It is a reflection of a dramatically shifting strategy that could change the course of space exploration and commercial spaceflight.
1. Accelerated Launch Cadence: A New Era of Rapid Testing
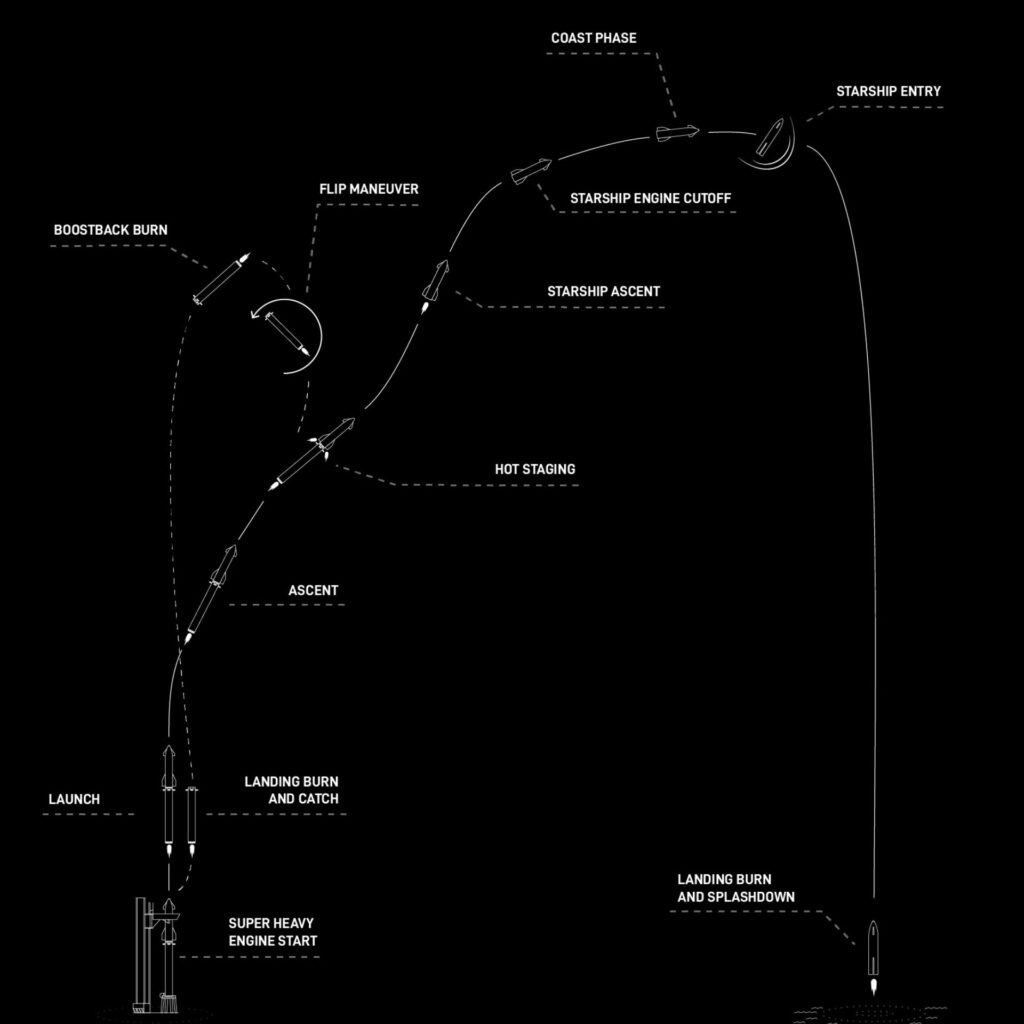
Perhaps the most striking development is SpaceX’s newfound ability to test Starship rockets at an unprecedented frequency. November’s sixth test follows just a month after the fifth flight, which itself was a breakthrough. Notably, the fifth flight included the first-ever successful return of Starship’s Super Heavy booster to the launch site via SpaceX’s innovative “chopstick” arms. This achievement, along with a controlled splashdown of the upper stage, was a massive milestone, proving that booster reusability is becoming a reality for the company.
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has expedited its regulatory approval process, enabling SpaceX to schedule consecutive tests. This streamlined approval system has significantly reduced delays that previously forced SpaceX to wait months between launches. As TechCrunch noted, this high-frequency testing strategy could allow the company to continuously refine the vehicle’s design and operation, pushing it closer to regular, operational flights.
2. Testing New Technologies: Reusability and Performance at the Forefront
The sixth flight is not just another chance to test a booster catch; SpaceX is upping the ante by introducing several cutting-edge technologies. One of the most critical objectives is the Raptor engine relight capability, a game-changer for future missions. This test will involve igniting one of the Starship’s Raptor vacuum engines during the coast phase, demonstrating the ability to perform de-orbit burns and controlled reentries—vital for future orbital missions and, eventually, crewed flights.
Thermal protection is another area of focus. The company will experiment with new secondary heat shield materials, including removing sections of tiles to assess their performance during reentry. This data is crucial as SpaceX looks to enhance Starship’s re-usability, which is fundamental for its ambitions to send humans to the Moon, Mars, and beyond. As Spaceflight Now reports, SpaceX will also perform tests on higher-angle-of-attack maneuvers to refine the vehicle’s landing profile, adding stress to the flaps that control descent, which is key for precise landings in future missions.
These tests reflect a clear focus on increasing the vehicle’s durability and reliability—not just for suborbital missions but for full-scale orbital flights.
3. Strategic Upgrades for the Future
While each flight offers the opportunity to gather valuable data, the real impact of these tests will be seen in future upgrades to the Starship system. As TechCrunch reports, engineers are introducing several system upgrades for the sixth flight, including more redundant propulsion systems and improved software controls. These enhancements are designed to improve both safety and performance during launch and recovery operations.
The results from this mission will also inform the next major phase of the program: Flight 7, which is expected to include significant upgrades. These could include redesigned flaps, larger propellant tanks, and improved thermal protection systems. SpaceX is aiming to use these insights to create a fully reusable rocket system that could launch multiple times in a day, effectively revolutionizing space access.
What This Means for SpaceX’s Future
These tests are a pivotal part of SpaceX’s larger strategy to dominate both government and commercial space sectors. Dr. Kent Chojancki, deputy program manager for NASA’s Human Landing System, explained that the success of Starship’s tests is critical for the Artemis program, which relies on Starship to carry astronauts to the Moon. He highlighted that a rapid iteration process like SpaceX’s will play a crucial role in meeting the tight timelines for these missions.
At the same time, experts like Margarita Polishchuk from Clay suggest that SpaceX’s ability to test and improve its system so rapidly could position it ahead of competitors like Blue Origin and Boeing. As Polishchuk points out, the pace of SpaceX’s testing cycle could force rivals to accelerate their own timelines in order to stay competitive in the space race.
SpaceX’s success with these tests could also have significant financial implications. As more successful tests are conducted, investor confidence will likely increase, bringing in more private and governmental partnerships. Analysts believe that SpaceX’s innovations could reshape the commercial spaceflight industry, potentially attracting even more lucrative contracts and support for its long-term goals.
SpaceX’s Starship program is entering a new phase, marked by rapid testing, technological advancements, and strategic upgrades. The upcoming sixth flight test on November 18, 2024, represents a critical step toward achieving the company’s long-term goals of full re-usability and human space exploration. As SpaceX continues to break new ground, it will be fascinating to see how these changes influence not only its future flights but also the broader space industry